Church: Difference between revisions
IanMaitland (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
IanMaitland (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Church Structure== | ==Church Structure== | ||
[[File: | [[File:ChurchDiagram.jpeg|left|thumb|Typical Church Floor Plan]] | ||
The basic structure of a church can be broken down into several sections: the Narthex, Nave, Crossing, Transept, Sanctuary, and Altar. | The basic structure of a church can be broken down into several sections: the Narthex, Nave, Crossing, Transept, Sanctuary, and Altar. | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
===Altar=== | ===Altar=== | ||
The main altar of a church is where the ritual of the eucharist is performed. It is located in the eastern section of the church to symbolize the coming of Christ in the rising of the sun and this is the reason churches are built facing the east. | The main altar of a church is where the ritual of the eucharist is performed. It is located in the eastern section of the church to symbolize the coming of Christ in the rising of the sun and this is the reason churches are built facing the east. | ||
===Sacristy=== | |||
The sacristy is located behind the apse and is where the materials for communion are stored. This is also where the priest will enter from and exit to before and after a mass. | |||
==Church Architecture== | ==Church Architecture== | ||
Latest revision as of 12:03, 8 November 2013

A Venetian church, or chiesa in Italian, is a house of worship for believers of the Christian faith. Churches are named after the patron saint for which they are built.
Church Structure
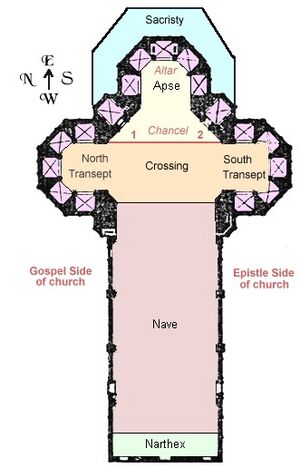
The basic structure of a church can be broken down into several sections: the Narthex, Nave, Crossing, Transept, Sanctuary, and Altar.
Narthex
The narthex or vestibule of a church is the entranceway into the main hall or nave. Narthexes are traditionally located on the western side of a church across from the main altar. Narthexes can be located inside or outside a church and, in the case of the latter, they are usually little more than a covered porch area.
Traditionally characterized by high ceilings and home to the pew, the nave refers to the main body of the church. This is the area of the church that is home to most of the floor artifacts in Venetian churches and, being the most inhabited, poses the most danger to these works of art.
Crossing
The crossing of a church is the oft domed area of the church where the transepts, chancel, and nave all intersect.
Transept
The transept is located across the line formed by the nave and chancel, separating the two. The transept is divided into the north and south transept with each one serving a different purpose specific to the church.
Chancel
The chancel refers to the east-most part of a church. This area is home to the main altar of the church and is where a church official would conduct mass and to give the eucharist. A separate section for the choir is present in some churches but is still located within the chancel.
Altar
The main altar of a church is where the ritual of the eucharist is performed. It is located in the eastern section of the church to symbolize the coming of Christ in the rising of the sun and this is the reason churches are built facing the east.
Sacristy
The sacristy is located behind the apse and is where the materials for communion are stored. This is also where the priest will enter from and exit to before and after a mass.
Church Architecture
The churches of Venice vary in many ways, but one subtle form is the layout of the floor. There are two variants of floor design, namely the latin cross and the greek cross. The latin cross is characterized by forming a traditional cross where the transept intersects the nave and chancel. The transepts are much smaller compared to the nave and located closer to the chancel. The greek cross has equal area for all floor sections and the transept intersects closer to the center of the nave and chancel.
A more visible difference in Venetian churches is shown in the many different architectural styles including Gothic, Byzantine, Baroque, and Renaissance. Due to Venice’s close proximity to more middle eastern areas it is no surprise that influences of architectural style were allowed to mix. Churches can express characteristics of one or more styles separating Venetian churches from the mostly western designs of Europe.
Many churches in Venice also function as more than a traditional church. There are often convents or bell towers attached, or in close proximity to, the churches.
Management
A church is often home to and operated by one or more priests. They conduct masses and are responsible for the general well-being of the church. Also before the age of automation, they were in charge of ringing the bells if the church had a bell tower. When a church is connected to a convent, the members of the convent would also be responsible for the affiliated church.