Wellhead
This page contains information about a typical Venetian wellhead.
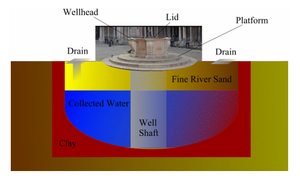
In the 16th century, Venetians built well systems to collect and filter rain to store as freshwater. The general design of a well and cistern typically includes a clay basin that stores rainwater. This water collects through street-level drains, filters through fine river sand, and then accumulates in the basin. There is a brick or stonewall well shaft that allows access to the water from the street level. These wells served as sources of fresh water in Venice. The water is retrieved from a structure called a wellhead. This is the only exposed part of the well. The wellhead appears as a circular basin with a lid above ground. (Thomollari, 2004)
Materials
Wellhead
All but two of the 217 public wellheads cataloged are composed exclusively of Istria stone, Red Verona marble, or White Verona marble. Istria is stone the most common material, accounting for 79 percent of the wellheads cataloged. Istria is followed by 14 percent Red Verona marble, and seven percent White Verona marble[2]. Istria stone is a type of limestone that has a gray-green or yellowish color. Lengthy exposure to the atmosphere causes the stone to obtain a whitish appearance through a process called “whitewashing.” Unfortunately, this also makes Istria stone a prime candidate for exfoliation. Verona marble is a sedimentary rock composed of organic limestone and fossils. It has either a reddish or whitish color depending on the carbon compounds it contains.

Lid
Well Shaft
While functioning as Venetians main water supply, the actual well shaft that extended from the wellhead to the cistern was made from bricks and lined with a layer of impermeable clay[3].
Cistern
The cisterns were made with large stones and then lined with impermeable clay that prevented the fresh water from leaking out and more importantly prevented salt water from leaking in and contaminating the water supply[4].
Current Water Supply
Venice is now supplied with water from the mainland, traveling underground through pipes from the commune Trebaseleghe which is filled by 120 artisan wells[5].
Public Art
Conservation & Restoration
See also
References
- ↑ Blackwell, Lewis et al. Preserving Venetian Wellheads. 2000. Pg 21
- ↑ Blackwell, Lewis et al. Preserving Venetian Wellheads. 2000. Pg 26 – 27
- ↑ Insula spa and Matteo Alemanno, Venice Preservation and Urban Maintenance( Venice, Italy: Grafiche Veneziane)
- ↑ Insula spa and Matteo Alemanno, Venice Preservation and Urban Maintenance( Venice, Italy: Grafiche Veneziane)
- ↑ Venice. The 1911 Classic Encyclepedia. October 21, 2006. http://www.1911encyclopedia.org/Venice
Bibliography
NULL